Structure¶
A class with no objects is called abstract class
Structures between classes¶
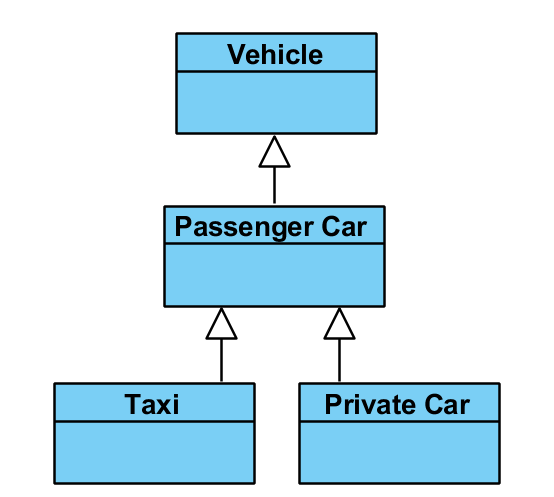
Generalization Structure¶
Generalization: A general class (the super class) describes properties common to a group of specialized classes (the subclasses)
Specialized Classes are subclasses
Generalized classes are superclasses
Example¶
The classes “Taxi” and “Private Car” might be specializations of the general class “Passenger Car” which might be a specialization of the general class “Vehicle”
Think programming!
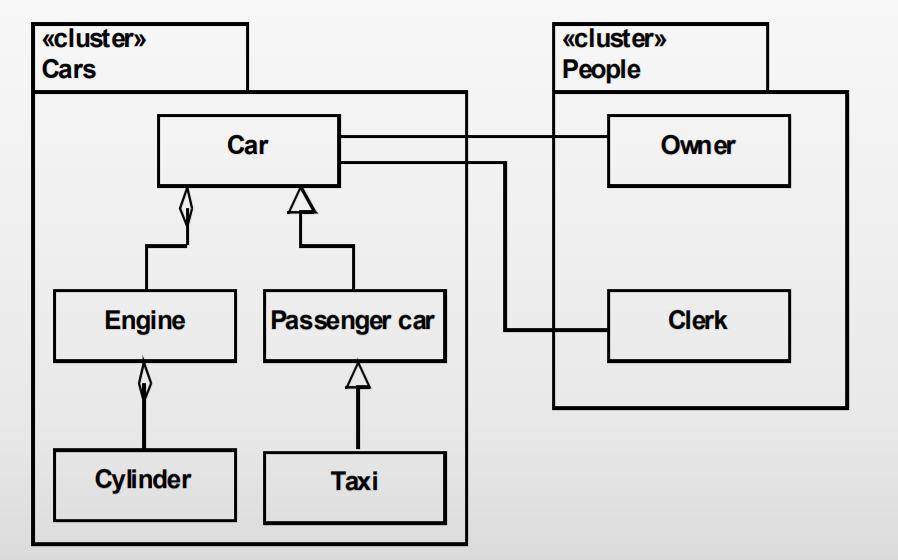
Cluster Structure¶
Cluster: Collection of related classes
Example¶
From an automobile register
Structures between objects¶
Two types: aggregation and association.
Aggregation Structure¶
Aggregation: A superior object (the whole) consists of a number of inferior objects (the parts)
See the picture below, “Car” consists of “Engine” which consists of “Cylinder”
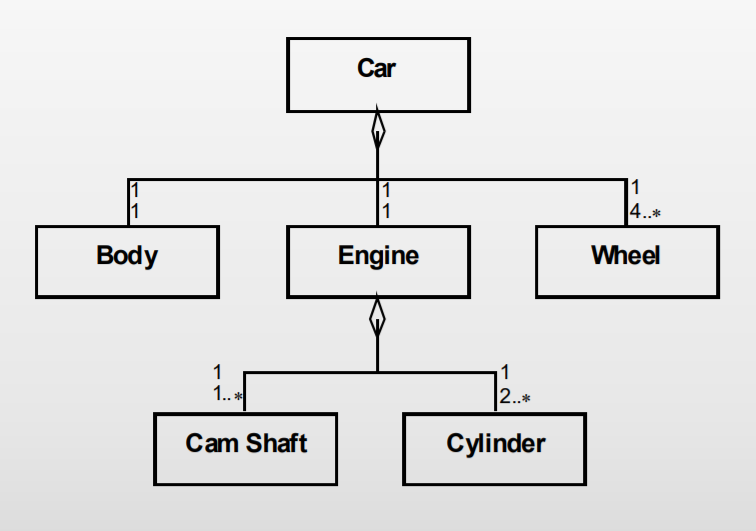
An Engine consists of at least 2 Cylinder's, this is marked by the 2...* and is called multiplicity
Association Structure¶
Association: A meaningful relation between a number of objects
For example, maybe a car is owned by one or more people, and a Person owns 0 or more cars. It It makes no sense to say that a person contains a car.

We can name the association, for example call this line “ownership” (This is often because we a missing a class though)
Find candidates for structure¶
Identify Generalizations¶
First approach; we take every pair and determine if one of the two is a generalization of the other
Second approach; we determine if a relevant generalization exists for pairs of selected classes.
Third approach; we take each of the selected classes and attempt to define a relevant generalization or specialization.
Identify Aggregations¶
To find candidates for aggregation, systematically examine selected classes individually in pairs.
There are three typical applications of aggregation structure:
- Whole-Part; the whole is the sum of the parts
- Container-Content; the whole is a container for the parts
- Union-Member; the whole is an organized union of members
The whole is considered to be superior to its parts. (Vertical placement in the class diagram)
Identify Associations¶
Look at remaining class pairs to see if the can be meaningfully related.
Identify Clusters¶
To increase the diagrams clarity
Can use other structures as a starting point for generating clusters.
It is NOT allowed to place a class in 2 different clusters!